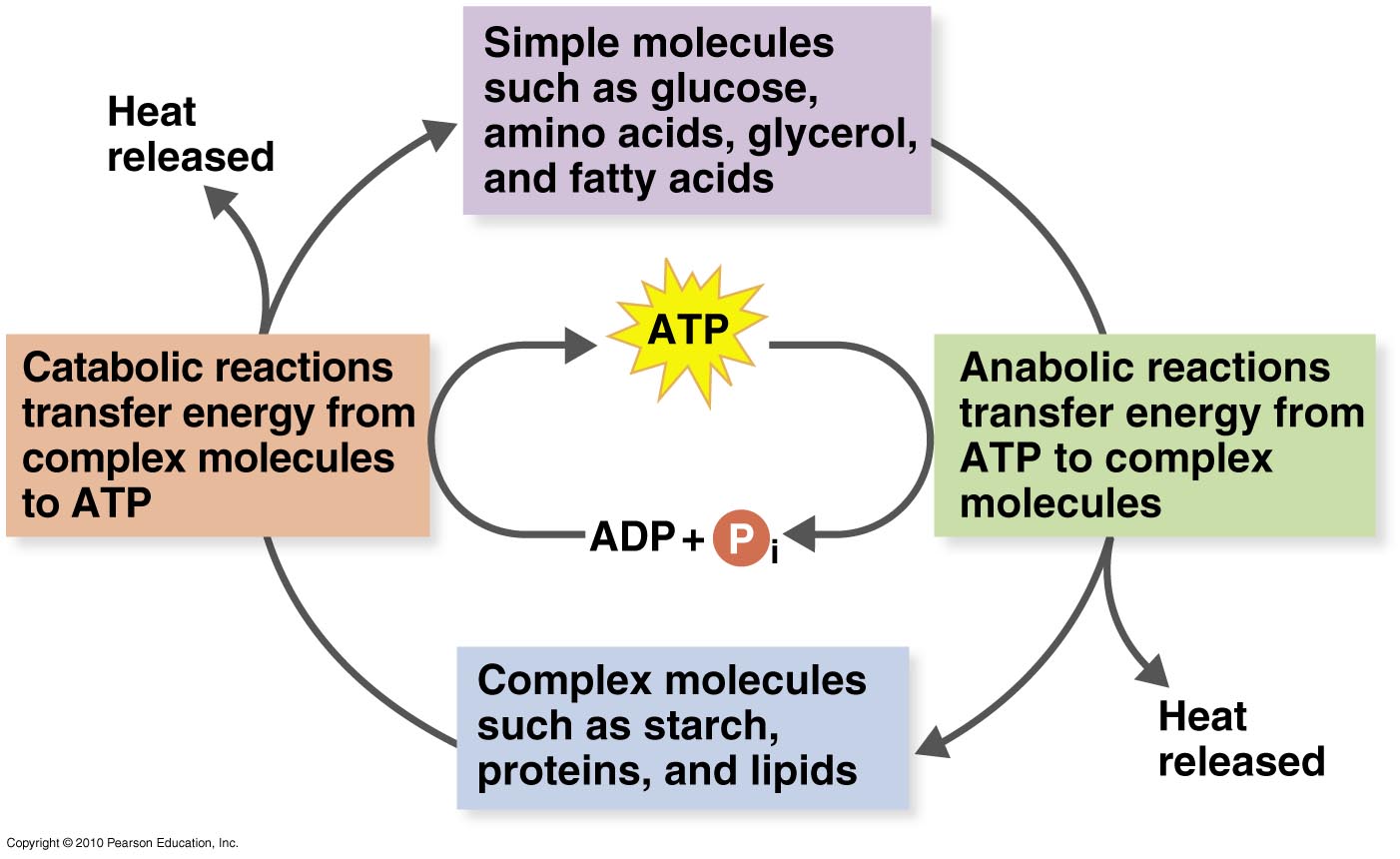
Catabolism is the opposite of anabolism which involves the synthesis of large molecules from smaller molecules and is endergonic as energy is used out. One may also ask, are catabolic pathways spontaneous? Anabolic pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules.
Are metabolic pathways endergonic or exergonic?
Are metabolic pathways Endergonic? Cellular processes such as the building or breaking down of complex molecules occur through series of stepwise, interconnected chemical reactions called metabolic pathways. Reactions that are spontaneous and release energy are exergonic reactions, whereas endergonic reactions require energy to proceed.
Why are catabolic and anabolic reactions exergonic?
That is why for most of the times, a catabolic reaction is exergonic. When an anabolic reaction occurs, smaller molecules or atoms form a large molecule.
What is an example of a catabolic process?
Examples of catabolic processes include glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, the breakdown of muscle protein in order to use amino acids as substrates for gluconeogenesis, the breakdown of fat in adipose tissue to fatty acids, and oxidative deamination of neurotransmitters by monoamine oxidase. What is an example of dehydration synthesis?
Can endergonic reactions take place without free energy?
An endergonic reaction will not take place on its own without the addition of free energy. Let’s revisit the example of the synthesis and breakdown of the food molecule, glucose. Remember that the building of complex molecules, such as sugars, from simpler ones is an anabolic process and requires energy.
What happens when a catabolic reaction breaks down?
Is anabolism an energonic or exergonic bond?
About this website
Are catabolic reactions exergonic or endergonic?
exergonicCatabolic reactions give out energy. They are exergonic. In a catabolic reaction large molecules are broken down into smaller ones.
Is catabolic endergonic?
Catabolism is the opposite of anabolism which involves the synthesis of large molecules from smaller molecules and is endergonic as energy is used out. Both anabolic and catabolic reactions often involve the use of a catalyst in the form of an enzyme, for example Rubisco in photosynthesis.
Is endergonic anabolic or catabolic?
anabolismEndergonic is a reaction that consumes energy and is involved in anabolism. Exergonic is a reaction that releases energy and is involved in catabolism.
Is catabolism and exergonic the same?
catabolism, the sequences of enzyme-catalyzed reactions by which relatively large molecules in living cells are broken down, or degraded. Part of the chemical energy released during catabolic processes is conserved in the form of energy-rich compounds (e.g., adenosine triphosphate [ATP]).
Do catabolic pathways require energy?
Anabolic pathways are those that require energy to synthesize larger molecules. Catabolic pathways are those that generate energy by breaking down larger molecules. Both types of pathways are required for maintaining the cell's energy balance.
Which type of reaction is endergonic?
In chemical thermodynamics, an endergonic reaction (also called a heat absorbing nonspontaneous reaction or an unfavorable reaction) is a chemical reaction in which the standard change in free energy is positive, and an additional driving force is needed to perform this reaction.
Are anabolic reactions exergonic or endergonic?
endergonic reactionsAnabolic reactions are endergonic reactions, meaning that they require an input of energy. Catabolism is the process of breaking down complex molecules into simpler molecules.
Are catabolic reactions endothermic?
Exothermic reactions in organisms are called catabolic reactions. These reactions break down molecules into smaller units and release energy.
What are exergonic and endergonic reactions?
Endergonic reactions require energy input to take simple, low energy reactants and build complex, high energy products. Exergonic reactions release the energy bound up in the reactants and yield simpler, low energy products.
Which are catabolic pathways?
Catabolic pathways involve the breakdown of nutrient molecules (Food: A, B, C) into usable forms (building blocks). In this process, energy is either stored in energy molecules for later use, or released as heat.
What is the difference between catabolic and anabolism?
Anabolism creates molecules the body needs for functionality and it uses energy in the process. Catabolism, on the other hand, breaks down complex molecules and releases energy which is available for the body to use.
What is anabolic and catabolic pathways?
Anabolic – this type of pathway requires energy and is used to build up large molecules from smaller ones (biosynthesis). Catabolic – this type of pathway releases energy and is used to break down large molecules into smaller ones (degradation).
Exothermic vs Exergonic and Endothermic vs Endergonic - CHEMISTRY COMMUNITY
Exothermic means the reaction releases heat. ΔH<0 Endothermic means the reaction requires heat. ΔH>0 Exergonic means the reaction is spontaneous, and releases energy.
Exergonic Vs Endergonic | Writing in Biology - UMass
Exergonic and endergonic reactions share similarities and differences. The most known definitions of exergonic and endergonic reactions is exergonic refers to a reaction that gives off energy, while endergonic reactions take in energy.
Endergonic and Exergonic vs Endothermic and Exothermic
One of the most common things I come across when working with students studying for the PCAT, DAT, AP, and college level chemistry courses is understanding the differences between endergonic and exergonic vs. endothermic and exothermic.
What is the relationship between metabolism and energy?
An important concept in the study of metabolism and energy is that of chemical equilibrium. Most chemical reactions are reversible. They can proceed in both directions, releasing energy into their environment in one direction, and absorbing it from the environment in the other direction ( see image below ).
Which chemical reactions release energy?
Exergonic reactions release energy; endergonic reactions require energy to proceed. Image credit: OpenStax Biology. The same is true for the chemical reactions involved in cell metabolism, such as the breaking down and building up of proteins into and from individual amino acids, respectively.
What is spontaneous reaction?
An important distinction must be drawn between the term spontaneous and the idea of a chemical reaction that occurs immediately. Contrary to the everyday use of the term, a spontaneous reaction is not one that suddenly or quickly occurs.
Is an endergonic reaction spontaneous?
These chemical reactions are what we refer to as endergonic reactions, and they are non-spontaneous. An endergonic reaction will not take place on its own without the addition of free energy.
Does sugar breakdown occur spontaneously?
Like the example of rust above, the breakdown of sugar involves spontaneous reactions, but these reactions don’t occur instantaneously .
Is sugar an anabolic process?
Remember that the building of complex molecules, such as sugars, from simpler ones is an anabolic process and requires energy. Therefore, the chemical reactions involved in anabolic processes are endergonic reactions.
What is an endergonic and exergonic reaction?
She has taught science courses at the high school, college, and graduate levels. Endergonic and exergonic are two types of chemical reactions, or processes, in thermochemistry or physical chemistry. The names describe what happens to energy during the reaction.
Is endergonic entropy positive?
The change in the standard Gibbs Free Energy (G) of an endergonic reaction is positive (greater than 0). The change in entropy (S) decreases. Endergonic reactions are not spontaneous. Examples of endergonic reactions include endothermic reactions, such as photosynthesis and the melting of ice into liquid water.
Is rust an exergonic reaction?
You cannot tell how quickly a reaction will occur based on whether it is endergonic or exergonic. Catalysts may be needed to cause the reaction to proceed at an observable rate. For example, rust formation (oxidation of iron) is an exergonic and exothermic reaction, yet it proceeds so slowly it's difficult to notice the release of heat to the environment.
What happens when a catabolic reaction breaks down?
When a catabolic reaction occurs, the large molecule is broken into smaller molecules with the breaking of chemical bonds that held them together. The bond is broken and energy stored in the bonds are released. That is why for most of the times, a catabolic reaction is exergonic.
Is anabolism an energonic or exergonic bond?
Catabolism breaks apart large molecules and anabolism creates large molecules. Catabolism is supposed to be exergonic, while anabolism is supposed to be energonic. Id on't really understand this. By definition a chemical bond is at an energy minimum.